How did I build Alippo's search from scratch? - Part 1
Search systems are crucial in most applications, enabling users to efficiently find products or information. At Alippo, we offer around 2,000 courses, so having an effective search system is essential for users to easily find courses that interest them.
Backstory
At Alippo, our philosophy is to leverage existing open-source projects whenever possible. We believe there’s no need to reinvent the wheel when brilliant solutions already exist. This approach applies to our search system as well.
In this series of articles, I’ll walk you through how we built Alippo’s search system. In this first article, I’ll discuss the basic architecture of our search system.
Choosing the Right Database
The first question we faced was which database to use. PostgreSQL, while excellent for general-purpose storage and management of structured or semi-structured data, is not optimized for full-text search operations. It lacks specialized indexing, ranking algorithms, and performance optimizations required for complex search queries and large-scale applications. Therefore, we chose Elasticsearch.
Why Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is preferred for building search systems over traditional databases like PostgreSQL or NoSQL databases due to its specialized full-text search capabilities, real-time indexing, horizontal scalability, advanced search features, analytics capabilities, schema-free design, and easy integration via its RESTful API.
Data Ingestion and Synchronization
With Elasticsearch as our chosen database, the next challenge was how to efficiently ingest data from our PostgreSQL database into Elasticsearch. We needed a solution that would not only handle one-time data ingestion but also keep Elasticsearch synchronized with our main database.
We discovered an excellent open-source project, mage2storefront, which synchronizes products, categories, and product-to-category links between a Magento2 API and a NoSQL database for Vue-storefront. We adapted this project to our needs, creating a server responsible for one-time data ingestion and ongoing data synchronization with our Elasticsearch cluster. By employing the abstract-factory pattern, we made it easy to add new search entities to our Elasticsearch index.
Maintaining Data Consistency
To maintain data consistency across both databases, we needed a way to connect our servers. We utilized Kafka, a powerful stream-processing platform, in conjunction with N8N, a free, self-hosted workflow automation tool. We set up a Kafka consumer node within N8N to listen to specific topics in the Kafka queue. Any changes in our main PostgreSQL database would be pushed to the queue, and N8N would notify our ingester server via webhooks.
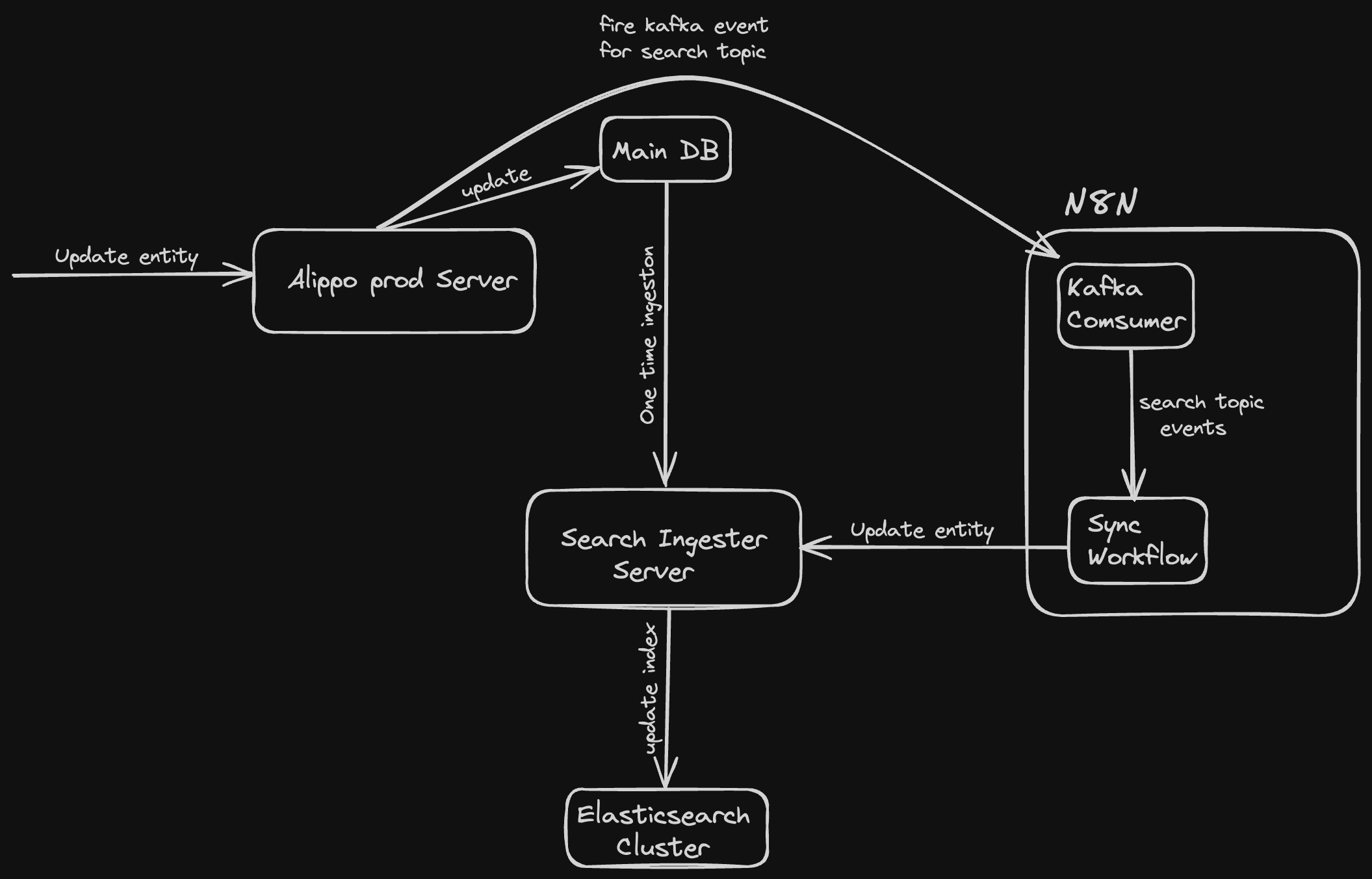
This was the basic high-level architecture of our search system. In the next part of this series, we’ll dive into the specifics of our Elasticsearch cluster index structure and explore the design choices we made in detail. How did we optimize for performance and relevance? What unique challenges did we face, and how did we overcome them? Stay tuned to discover the secrets behind Alippo’s powerful search capabilities!
Make sure you like, comment & share if you like!
Published on May 18, 2024